What is heritage?
It’s a set of assets acquired by inheritance and by title :
- set of family assets
- set of State assets
- set of municipal assets
A set of lifestyles, customs, knowledge, and degree of artistic, scientific, industrial
development, in an epoch, social group…
Set of assets (tangible as well as intangible) that have to do with the culture of a people, nation, city, society…
This concept is crucial because it implies the cultural identity of a people.
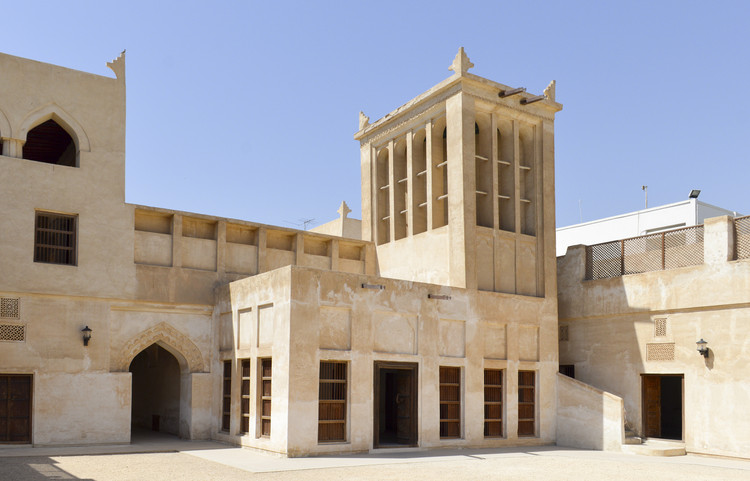

In the long run, architectural heritage is viewed as a tangible manifestation of cultural diversity. It traces the history of a country, molds its culture, and fosters continuity, stability, and communal cohesion.
People have always made a life with what was available, even in ancient times when there was less transportation and creativity. Its antecedents are the historical structures that have meaning in terms of art, design, technique, and culture. Some places still adhere to these principles of using vernacular building or living practices.
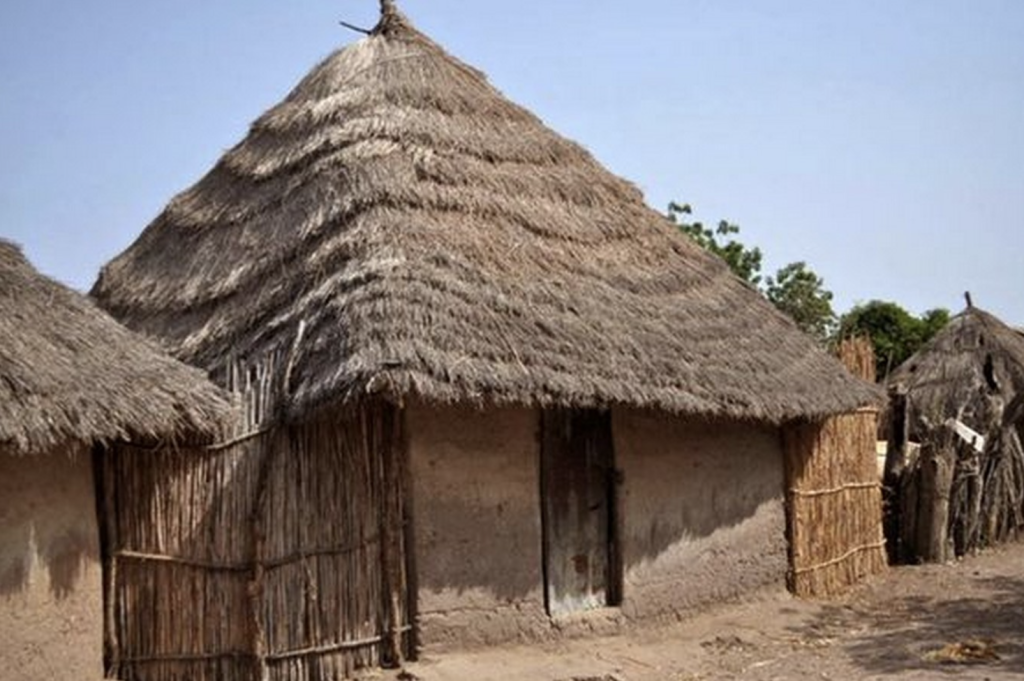

Cultural identity:
In 1972, UNESCO proposed a new classification of cultural assets:
- Monuments: architecture, sculpture, painting, archaeology, caverns, inscriptions, elements of universal value from the point of view of history, art, or science.
- Sets: groups of constructions whose architecture and integration with the landscape give them exceptional value from the historical, art, or scientific point of view.
- Places: works of man and nature with a universal value from the historical, aesthetic, ethnological, or anthropological point of view.

Why should we preserve heritage?
As a source of identity, heritage is valuable for empowering local communities and enabling vulnerable groups to participate fully in social and cultural life.
-The values of heritage:
- cultural value
- artistic value/aesthetic value
- historical value
- value of authenticity
- value of antiquity
- functional/social value
- economic value
What should be preserved?
1)- Values:
Protect the physical architectural heritage and its values (historic, artistic, antiquity, functional, economic…)
2)- Physical conservation:
- matter
- construction techniques
- shapes, dimensions
- colors, materials, textures
- character
- use
- environment
- meanings…
3)- Enhancement:
Make the building show and explain its values.
How to preserve it?
- Reversibility of the intervention.
- Preservation of the authenticity of the material document and character.
- Minimal intervention.
- Distinguishability and expressive actuality.
- Compatibility: material, structural, character, functional, etc.
- The durability of the intervention.
- Environmental and economic sustainability.
A living testament to the brilliance of our ancestors, the architectural legacy is one of the most significant material sources that records the personal, social, and cultural activities that occurred in the past.A historical environment that reflects a specific era is created by the building history, which adds to the place’s spatial value. Additionally, it helps to incorporate time into urban planning, which creates a sense of local identity.
It has become necessary for scholars and researchers to find ways and solutions to preserve heritage because of its importance to people and humanity as a whole. Given the importance of cultural and architectural heritage to the people in expressing their identity and the identity of their cultural and historical civilization.