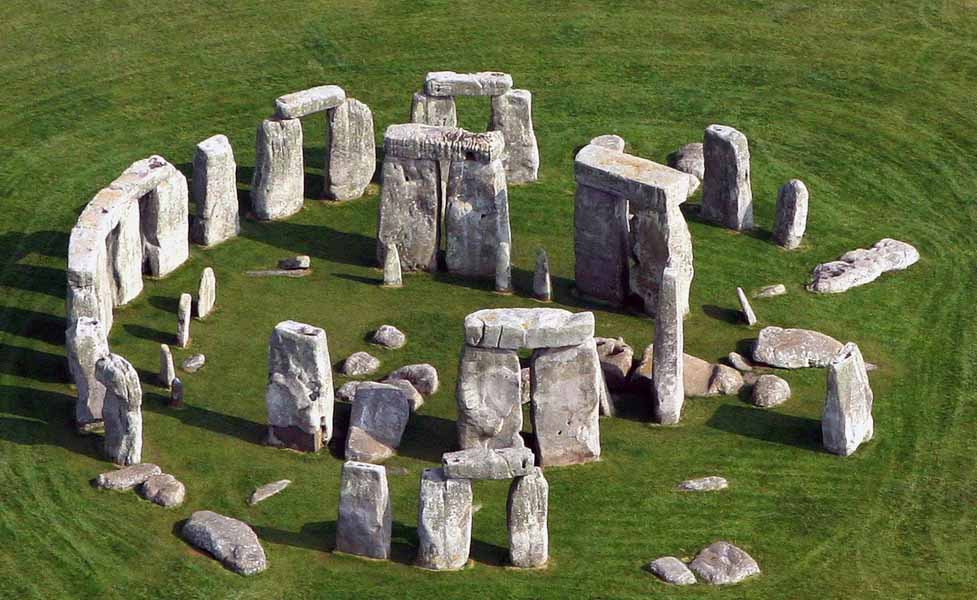
Pre-historical architecture(11,600 BCE to 3,500 BCE)
Includes monumental structures such as Stonehenge, cliff dwellings in the Americas, and thatch and mud structures lost t time.
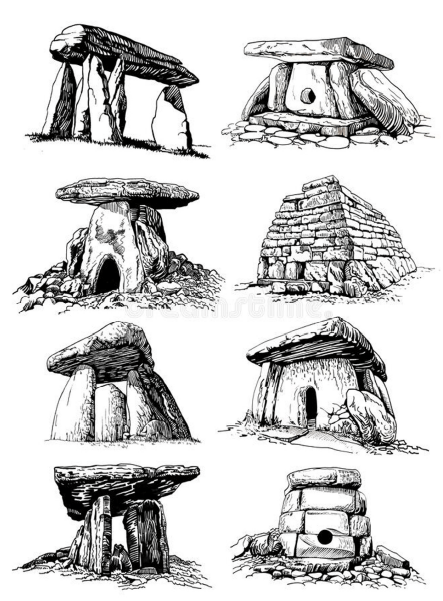


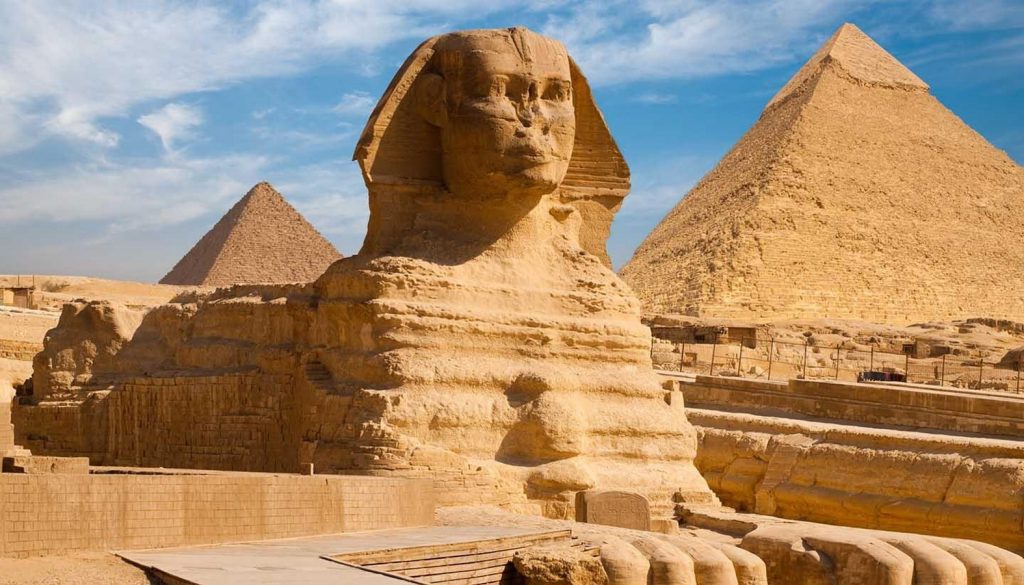
Egyptian architecture (3,500 BCE to 900 AD)
In ancient Egypt, powerful rulers constructed monumental pyramids, temples and shrines.

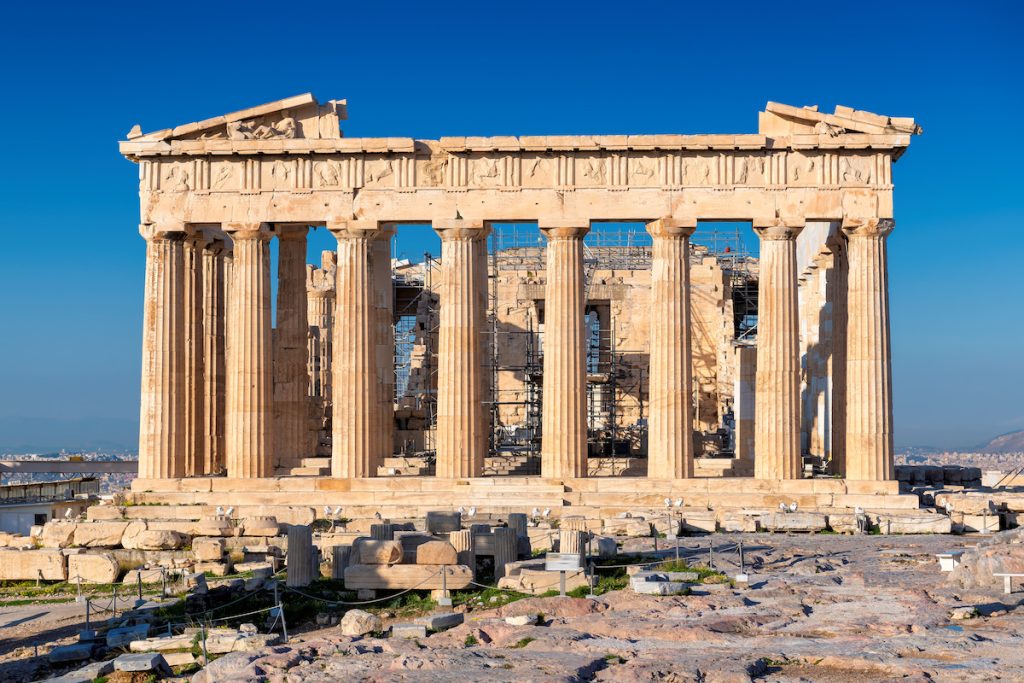
Classical architecture(850 AD to 476 AD)
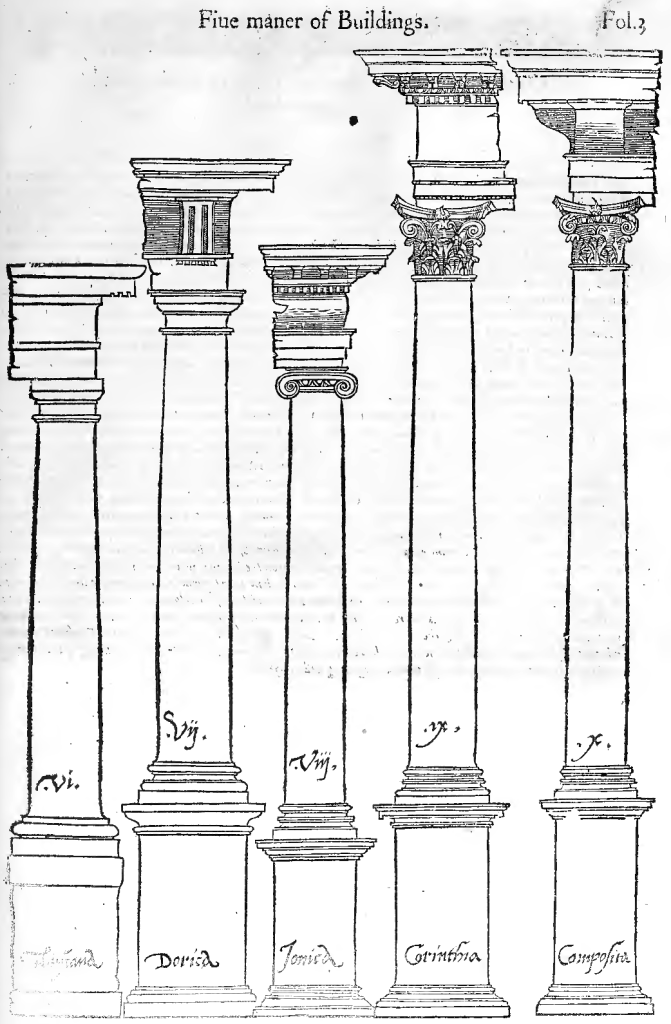
Usually denotes architecture that is more or less consciously derived from the principles of Geek and Roman architecture.

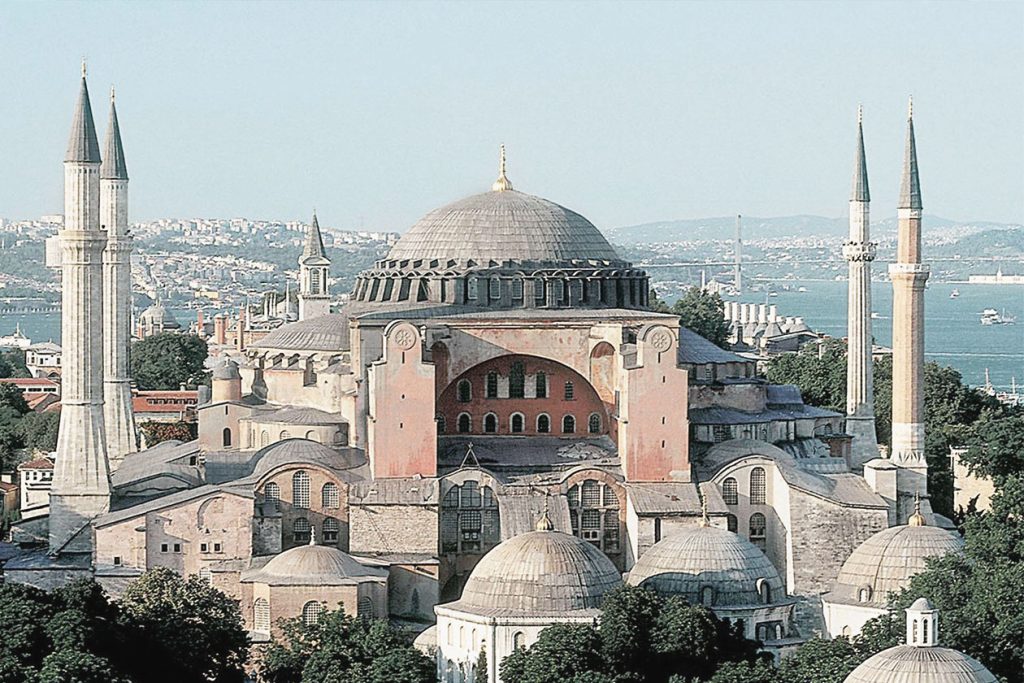
Early Christian and Medieval(373 AD to 500 AD)
It is also called Paleochristian art. European architecture moved from the rectangular basilica forms to the classically inspired Byzantine style.

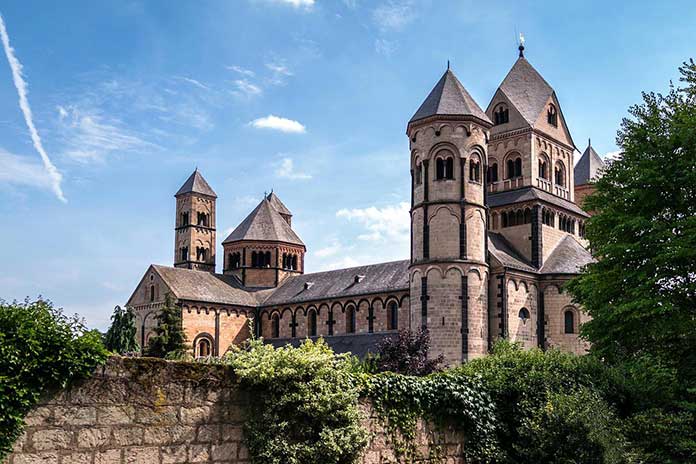
Romanesque architecture(500 AD to 1200 AD)
An architectural style of medieval Europe characterized by semi-circular arches

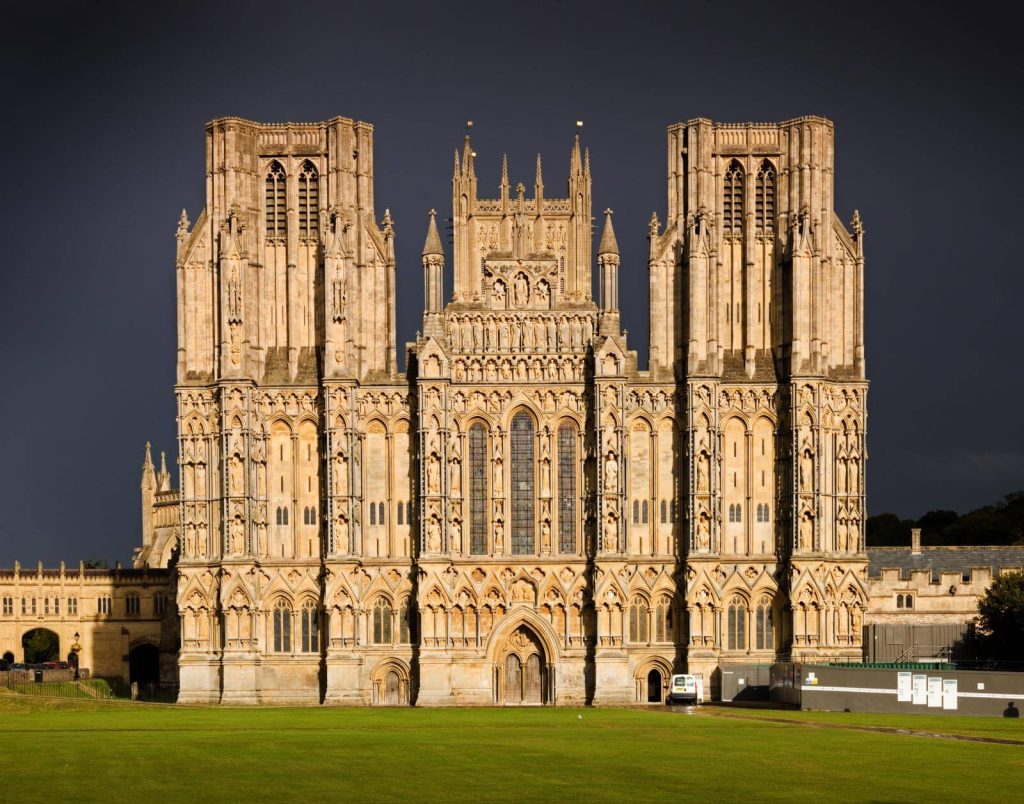
Gothic architecture(1100 AD to 1450 AD)
It is particularly a style of masonry building characterized by cavernous spaces with the expanse of walls broken up by overlaid tracery.

Renaissance architecture(1400 AD to 1600 AD)
The utilization of classical orders, mathematically exact height to width ratios, symmetry, proportion, and harmony are some of the distinguishing characteristics of Renaissance architecture. In inventive ways, columns, pediments, arches, and domes are used in structures of many kinds.
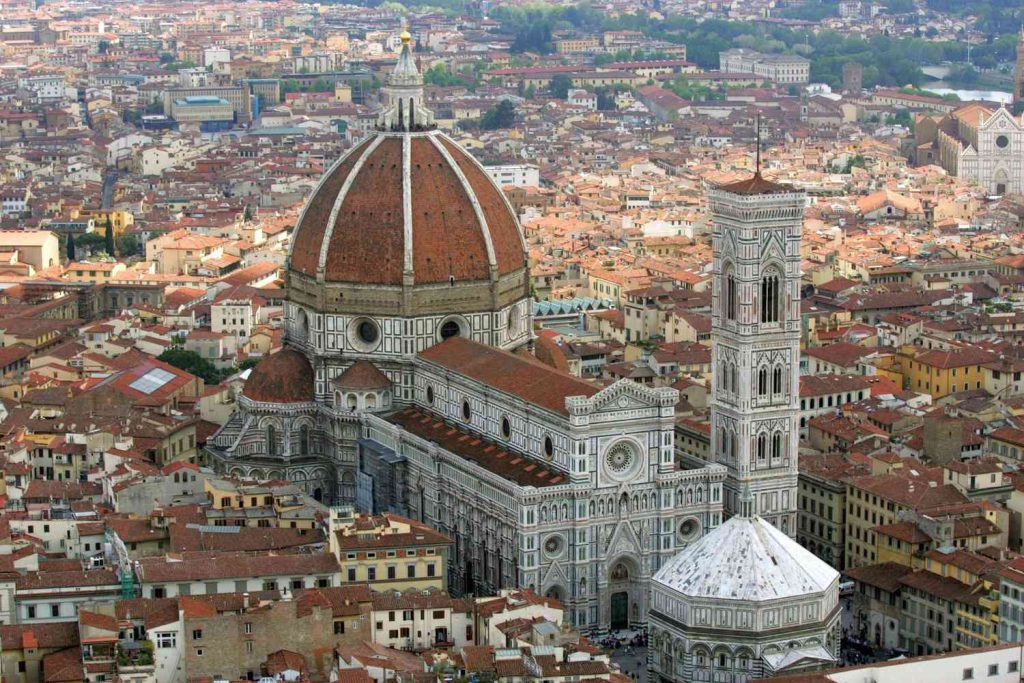

Baroque architecture(1600 AD to 1830 AD)
Baroque architecture is distinguished by dynamic patterns and intricate architectural plan forms that are typically based on the oval and meant to heighten feelings of motion and sensuality. The repetition, fragmentation, and distortion of Renaissance classical elements are frequently combined.
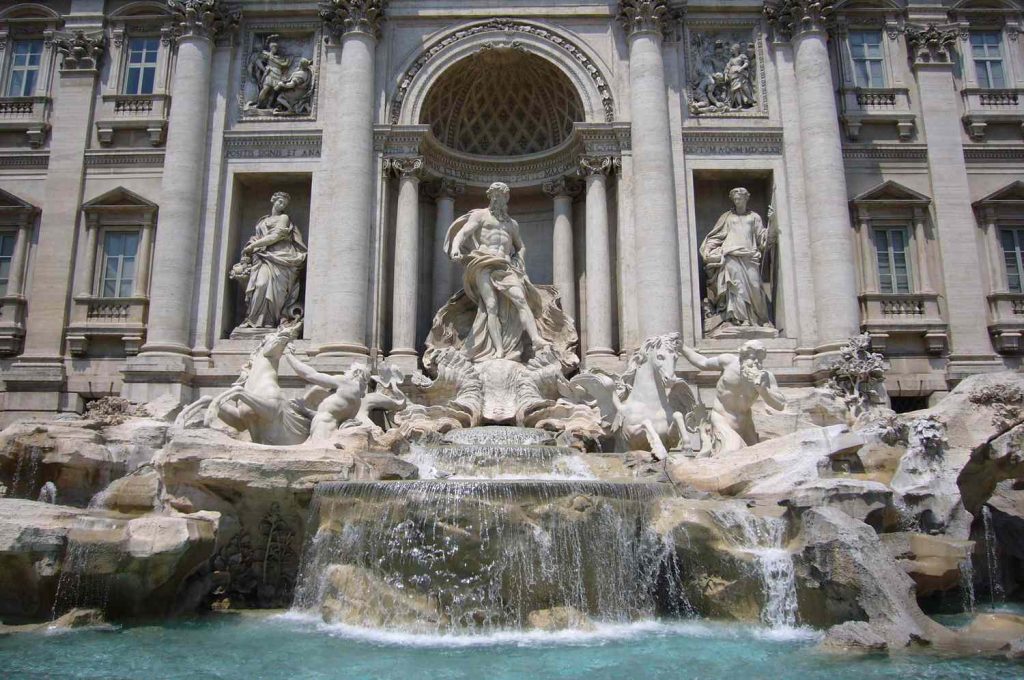

Rococco architecture(1650 AD to 1790 AD)
Rococo architecture is frequently associated with structures built in eighteenth-century France, but the style also impacted music, art, furniture, and silverware.

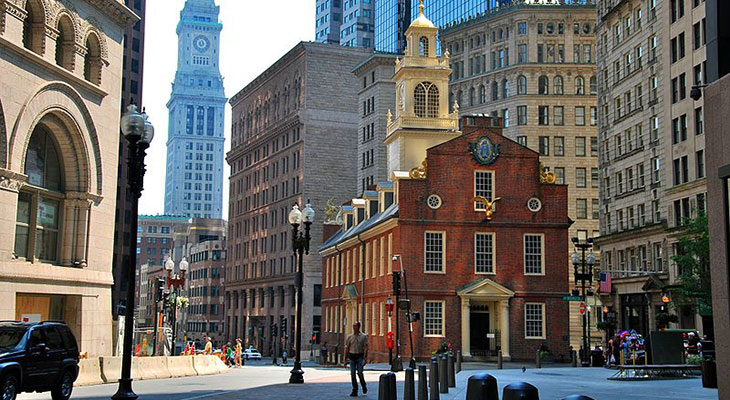
American clonial(1600 AD to 1780 AD)
Essentially refers to the English post-medieval style, the Dutch, French, and Spanish colonial styles, as well as the Georgian style—five different colonial architectural styles.

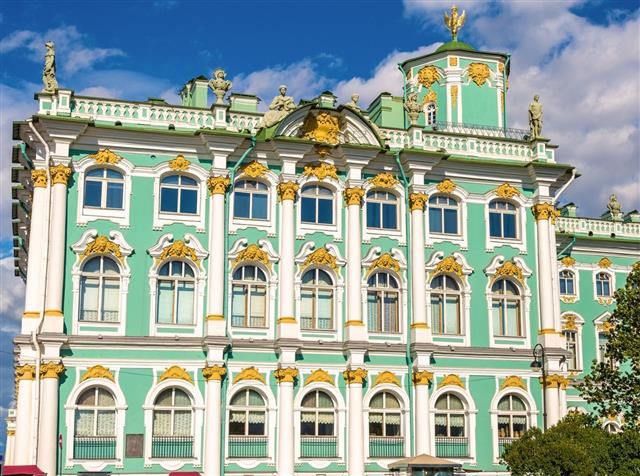
Georgian architecture (1720 AD to 1800 AD)
An architectural design known as Georgian architecture, which has its roots in 18th-century England, is defined by symmetry, balance, and proportion. This common architectural style can be seen all around the country, but it is most prevalent in the Northeast, particularly in New England.
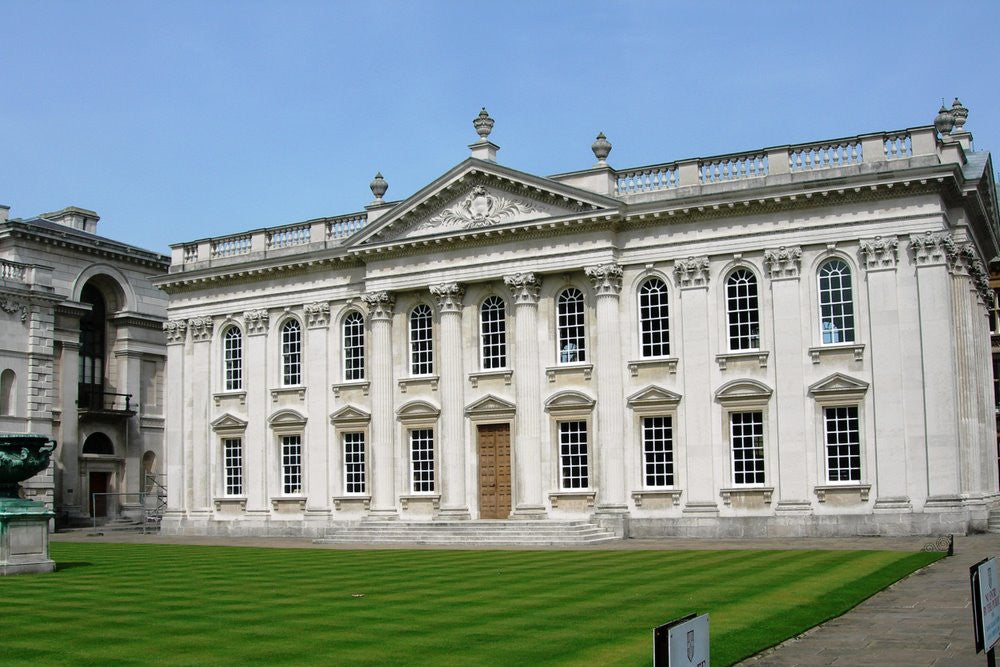

Neo-Classical(1730 AD to 1925 AD)
The grandeur of scale, simplicity of geometric forms, Greek detail—especially Doric, Roman detail, dramatic use of columns, and a propensity for blank walls are characteristics of neoclassical architecture. The new trend toward vintage simplicity was a response to the excesses of the Rococo style.
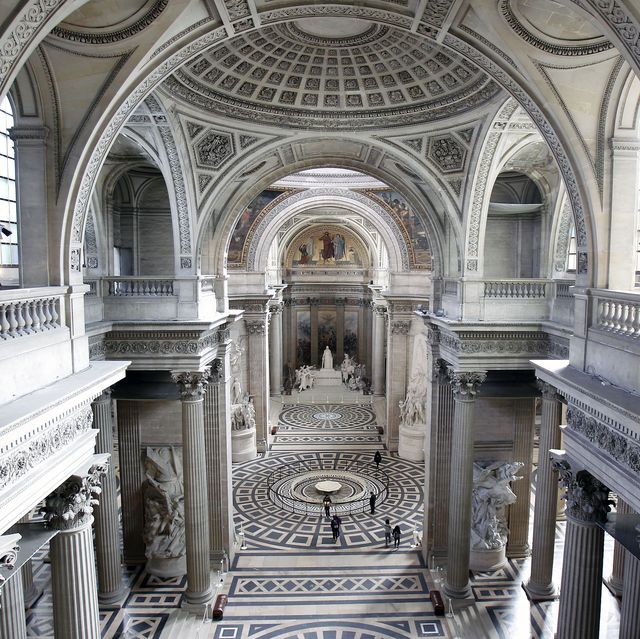

Geek revival(1790 AD to 1850 AD)
Greek Revival houses have symmetrical facades with rows of magnificent columns and low-pitched gable roofs influenced by classical architecture, particularly temples.

Victorian architecture(1840 AD to 1900 AD)
It happened during Queen Victoria’s reign. Many well-known architectural designs emerged during the Victorian era, including the Gothic revival, Italianate, Second Empire, Queen Anne, stick, Romanesque, and shingle styles.

Art nouveau(1890 AD to 1940 AD)
is distinguished by originality, the presence of rhythms, colors, and ornamentations that draw inspiration from plants, flowers, insects, and animals and that adds sensitivity to the daily decor.


Beaux Arts architecture(1895 AD to 1925 AD
The order, symmetry, formal design, grandiosity, and lavish adornment that define Beaux Arts. Balconies, columns, cornices, pilasters, balconies, balustrades, and triangular pediments are examples of architectural features.

Neo-gothic(1905 AD to 1930 AD)
It is distinguished by pointed arches, ribbed vaults, enormous stained-glass windows, flying buttresses (supporting stone arches), extravagant building embellishment like gargoyles or saint statues, and more.
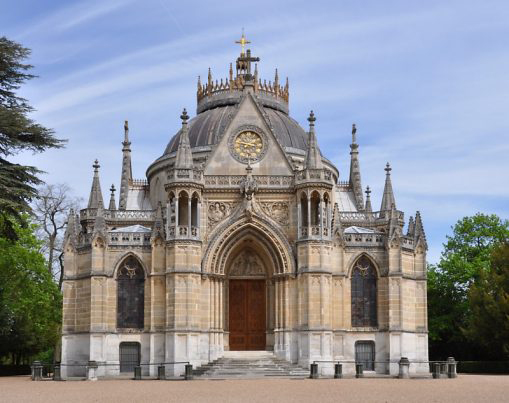

Art Deco architecture(1925 to 1937)
The refusal of straight angles: for corner buildings, the Art Decostyle favors cut or rounded corners. The use of disparate materials to design buildings: reinforced concrete is the most used material but it mixes with cut stone, brick or glass.
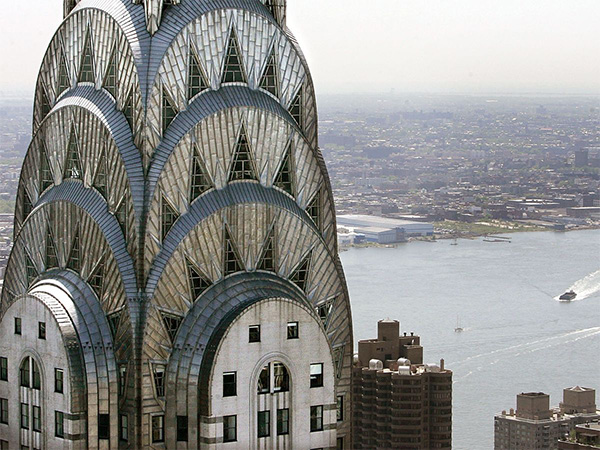

20th century trends in architecture(1900 to Present)
The century has seen dramatic changes and astonishing diversity. Twentieth century trends include Art Modern and the Bauhaus school, deconstructivism, formalism, modernism, structuralism, postmodernism and sustainable/ green architecture.


SOURCES:
https://www.britannica.com/art/Egyptian-architecture
https://www.thespruce.com/classical-architecture-4797909
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Early_Christian_art_and_architecture
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gothic_architecture
https://www.thespruce.com/what-is-renaissance-architecture-5186491